Finding subgraph isomorphisms in Rust
I am pleased to announce the release of vf2: a Rust implementation of the VF2 subgraph isomorphism algorithm [1]. It can find graph isomorphisms, subgraph isomorphisms, and induced subgraph isomorphisms. Graphs can be directed or undirected.
You can find more information in the GitHub repository.
Motivation
Subgraph matching is the task of finding instances of a query graph within a larger data graph. It is useful when searching for patterns in a graph structure, such as relationships in a social network. It is a fundamental problem in graph theory with applications in pattern recognition, databases, security, and biochemistry.
Consider a network like LinkedIn where each node is a person, and each edge represents a connection. You are tasked with finding cases where five software developers and a doctor all know each other. You can make a query graph with developers and a doctor, and search for instances of that query in the larger network.
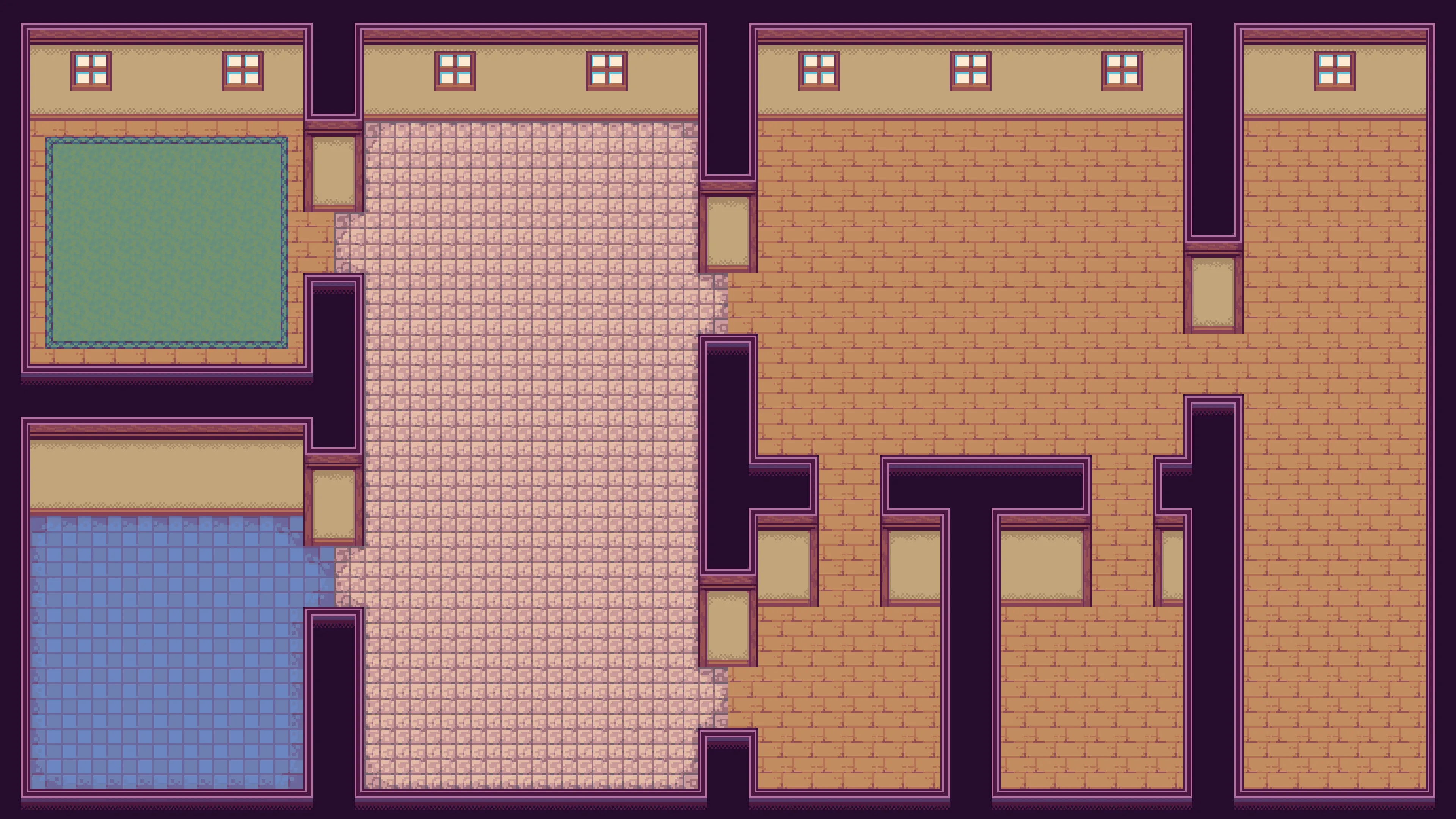
My use case is generating building layouts. I generate a graph representing which rooms must be adjacent and use subgraph matching to fit that into an existing layout. The rooms are then resized using simulated annealing. In this manner, the logical layout can be optimized independently of the physical layout.
What is a subgraph isomorphism?
A graph is a structure consisting of a set of objects where some pairs of objects are connected. A graph isomorphism is a one-to-one correspondence between two graphs such that objects connected in one are also connected in the other.
Graph isomorphism
For two graphs to be isomorphic, there must be a one-to-one correspondence between nodes such that neighbors in one are also neighbors in the other. The query and data graphs in the following image are isomorphic.
Subgraph isomorphism
It is often desirable to find instances of one graph within another. To do this, we search for subgraph isomorphisms. A subgraph isomorphism is when one graph is isomorphic to a subgraph of another. There are two subgraph isomorphisms in the following image.
Induced subgraph isomorphism
An induced subgraph isomorphism is the same as a subgraph isomorphism except that the subgraph must be induced. Edges in the data subgraph must also exist in the query graph.
Example
This example shows how to find subgraph isomorphisms. Please see the repository for usage instructions.
use petgraph::data::{Element, FromElements};
use petgraph::graph::DiGraph;
fn main() {
// Create query graph.
let query = DiGraph::<i32, ()>::from_elements([
Element::Node { weight: 0 },
Element::Node { weight: 1 },
Element::Edge { source: 0, target: 1, weight: () },
]);
// Create data graph.
let data = DiGraph::<i32, ()>::from_elements([
Element::Node { weight: 0 },
Element::Node { weight: 1 },
Element::Node { weight: 2 },
Element::Edge { source: 0, target: 1, weight: () },
Element::Edge { source: 1, target: 2, weight: () },
]);
// Find subgraph isomorphisms.
let isomorphisms = vf2::subgraph_isomorphisms(&query, &data).vec();
assert_eq!(isomorphisms, vec![vec![0, 1], vec![1, 2]]);
}
References
[1] L. P. Cordella, P. Foggia, C. Sansone, and M. Vento, “A (sub)graph isomorphism algorithm for matching large graphs,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 26, no. 10, pp. 1367–1372, Oct. 2004, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2004.75.
[2] A. Jüttner and P. Madarasi, “VF2++—An improved subgraph isomorphism algorithm,” Discrete Applied Mathematics, vol. 242, pp. 69–81, Jun. 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dam.2018.02.018.


